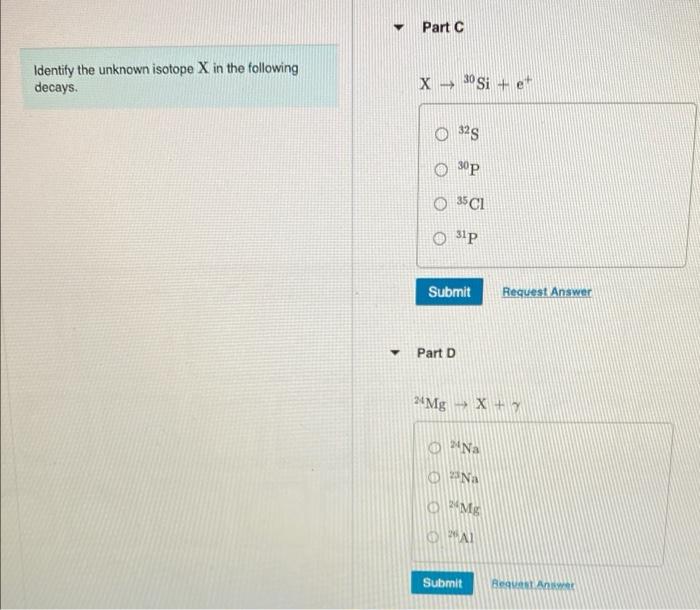
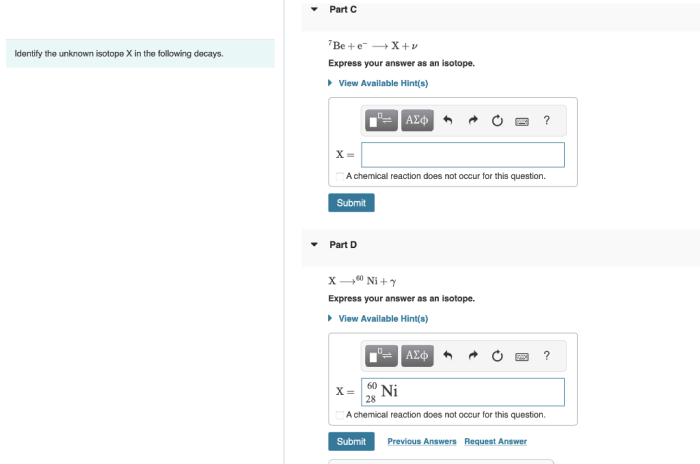
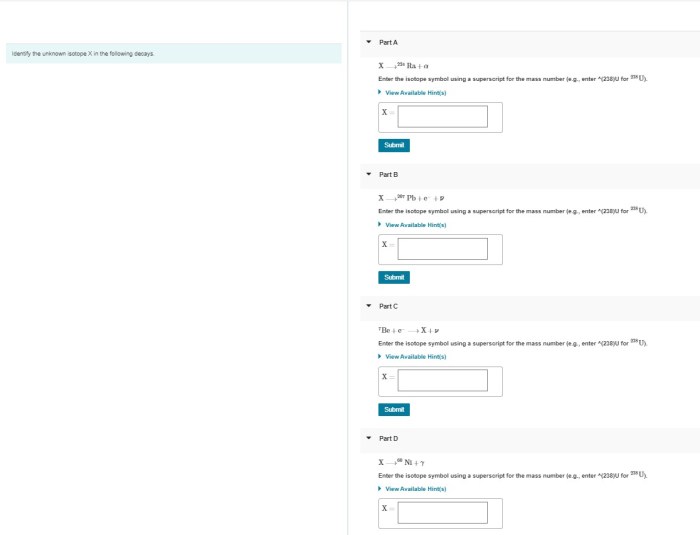
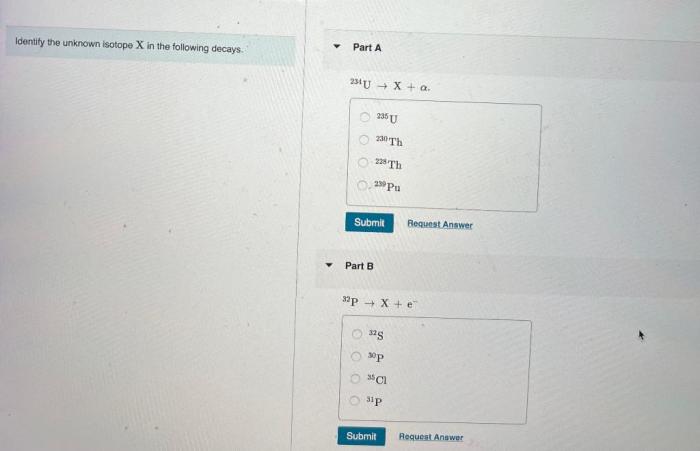
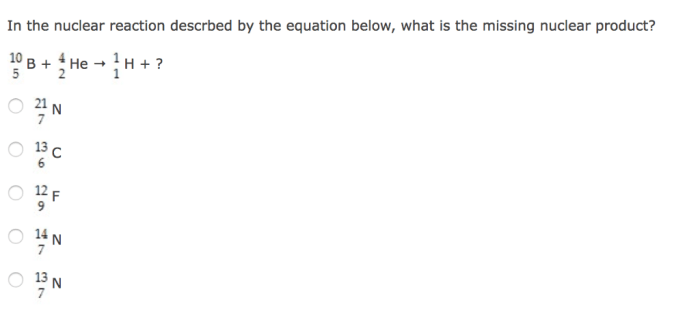Identify the unknown isotope x in the following decays. – Identifying the unknown isotope X in radioactive decays is a crucial process in nuclear physics and various scientific disciplines. By analyzing decay patterns, scientists can unravel the identity of isotopes and gain insights into their properties and applications. This article explores the techniques and significance of isotope identification, providing a comprehensive overview of this fascinating field.
Understanding the different types of radioactive decay, such as alpha, beta, and gamma decay, is essential for identifying isotopes. Each decay mode releases specific particles or energy, providing clues about the atomic number and mass of the decaying nucleus. By analyzing these decay patterns, scientists can construct decay chains and determine the identity of the unknown isotope X.
Isotope Identification: Identify The Unknown Isotope X In The Following Decays.
The identification of unknown isotopes is a crucial aspect of nuclear physics and various other scientific disciplines. It involves determining the atomic number, mass number, and nuclear properties of an unknown isotope based on its decay patterns and other characteristics.
There are several methods used to identify unknown isotopes, including:
Decay Chain Analysis
Decay chains are sequences of radioactive decays in which an unstable parent nucleus undergoes a series of transformations, emitting particles and energy until it reaches a stable daughter nucleus. By analyzing the decay chain, including the types of particles emitted, their energies, and the half-lives of the intermediate isotopes, it is possible to determine the identity of the unknown isotope.
For example, consider the decay chain of Uranium-238:
- Uranium-238 (α decay) → Thorium-234
- Thorium-234 (β decay) → Protactinium-234
- Protactinium-234 (β decay) → Uranium-234
- Uranium-234 (α decay) → Thorium-230
- …
Half-Life Measurements, Identify the unknown isotope x in the following decays.
Half-life is the time it takes for half of the atoms in a radioactive sample to decay. By measuring the half-life of an unknown isotope, it is possible to determine its identity. Different isotopes of the same element typically have different half-lives.
For example, Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5,730 years, while Carbon-12 is stable and does not decay.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of identifying unknown isotopes?
Identifying unknown isotopes is crucial for understanding the composition and behavior of matter, as well as for applications in various scientific fields. It allows scientists to study nuclear processes, trace the origins of elements, and develop new technologies.
How are decay chains used to identify isotopes?
Decay chains are sequences of radioactive decays that occur when an unstable isotope transforms into a more stable one. By analyzing the sequence of decays and the emitted particles, scientists can determine the identity of the original isotope and its decay products.
What role do half-life measurements play in isotope identification?
Half-life is the time it takes for half of a radioactive sample to decay. By measuring the half-life of an unknown isotope, scientists can determine its decay rate and use this information to identify the isotope.