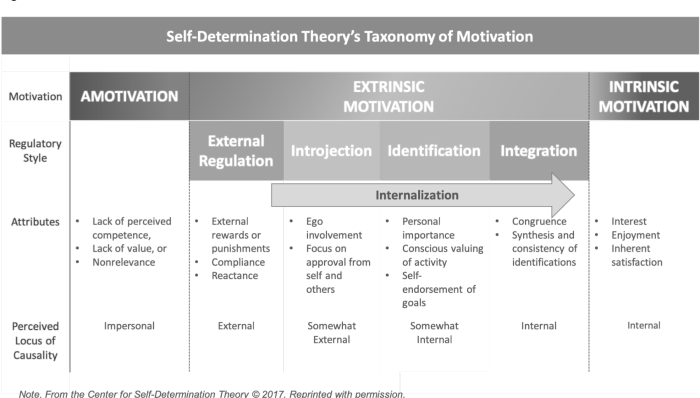
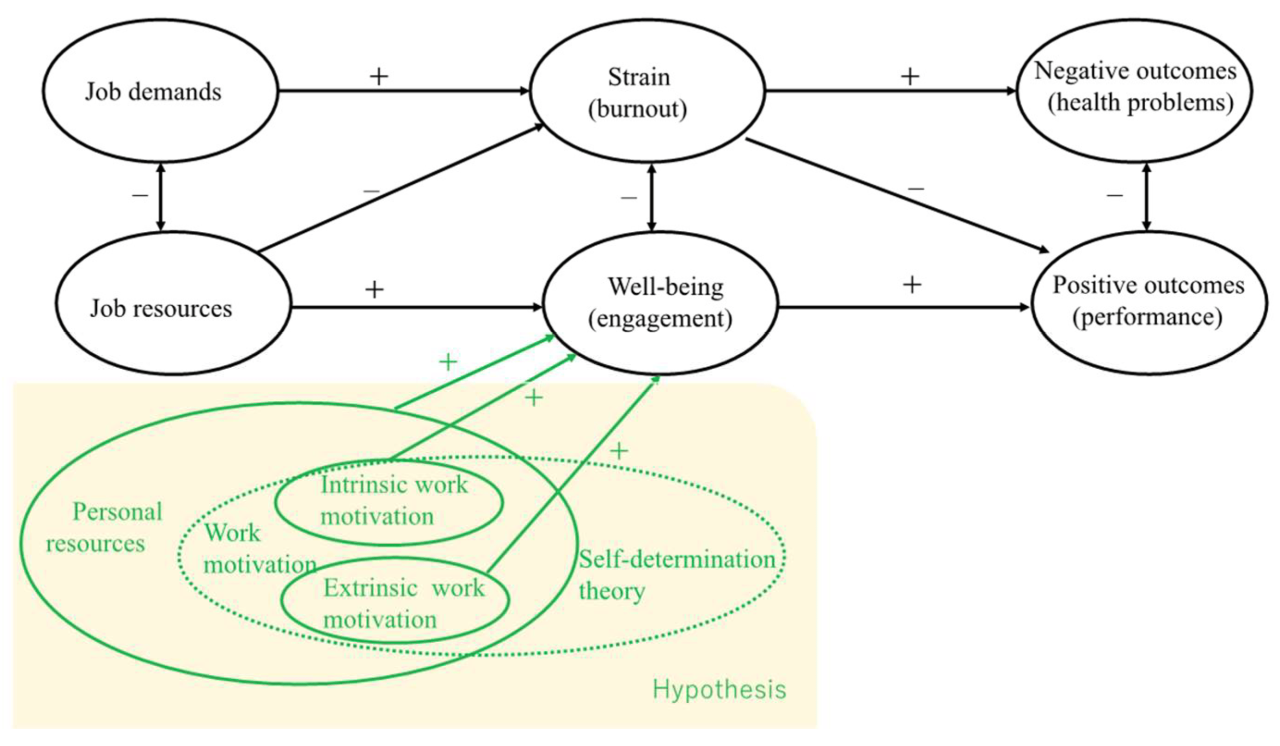
Research on intrinsic and extrinsic motivation contends that both forms of motivation play crucial roles in shaping learning and performance. Intrinsic motivation, driven by internal factors such as curiosity and enjoyment, fosters deep engagement and sustained effort. On the other hand, extrinsic motivation, fueled by external rewards or punishments, can provide short-term incentives but may undermine intrinsic motivation if overused.
This article delves into the intricacies of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation, exploring their distinct characteristics, impact on learning outcomes, and practical applications in educational settings. By understanding the nuances of each type of motivation, educators and learners can harness their potential to enhance learning experiences and optimize performance.
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation Concepts
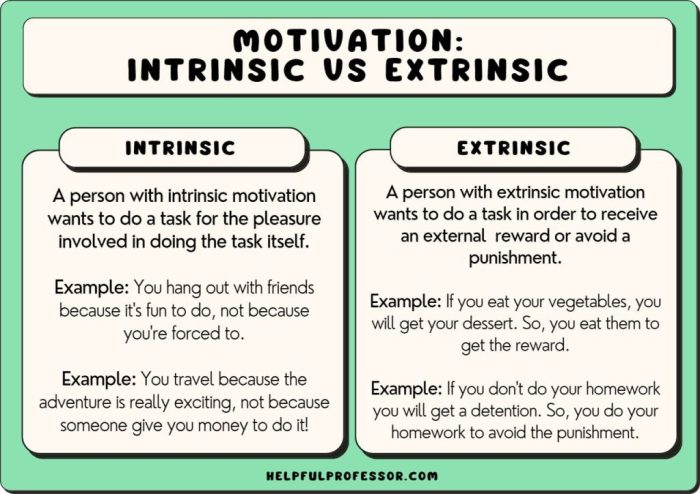
Motivation refers to the driving forces that prompt individuals to engage in specific actions or behaviors. Two primary types of motivation are intrinsic and extrinsic motivation.
Intrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation is driven by internal factors and arises from within the individual. It involves engaging in an activity for its own sake, without any external rewards or incentives. Examples include pursuing hobbies, learning new skills, or solving puzzles.
Extrinsic Motivation
Extrinsic motivation is influenced by external factors and arises from outside the individual. It involves engaging in an activity to obtain a specific reward or avoid a negative consequence. Examples include studying for a test to get a good grade, working to earn a salary, or exercising to lose weight.
Differences between Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation, Research on intrinsic and extrinsic motivation contends that
- Source:Intrinsic motivation is internal, while extrinsic motivation is external.
- Nature:Intrinsic motivation is autonomous, while extrinsic motivation is controlled.
- Sustainability:Intrinsic motivation is more sustainable and long-lasting, while extrinsic motivation can be more temporary.
- Impact:Intrinsic motivation leads to higher levels of engagement, creativity, and performance, while extrinsic motivation can sometimes lead to lower levels of engagement and performance.
FAQ Summary: Research On Intrinsic And Extrinsic Motivation Contends That
What is the key difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation?
Intrinsic motivation arises from internal factors such as enjoyment and curiosity, while extrinsic motivation is driven by external rewards or punishments.
How does intrinsic motivation impact learning?
Intrinsic motivation fosters deep engagement, sustained effort, and a desire for mastery.
Can extrinsic motivation be harmful?
Overuse of extrinsic motivation can undermine intrinsic motivation and lead to a focus on short-term rewards rather than long-term learning goals.