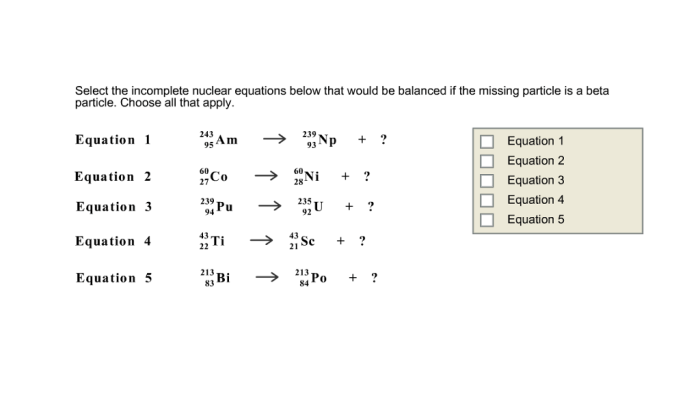
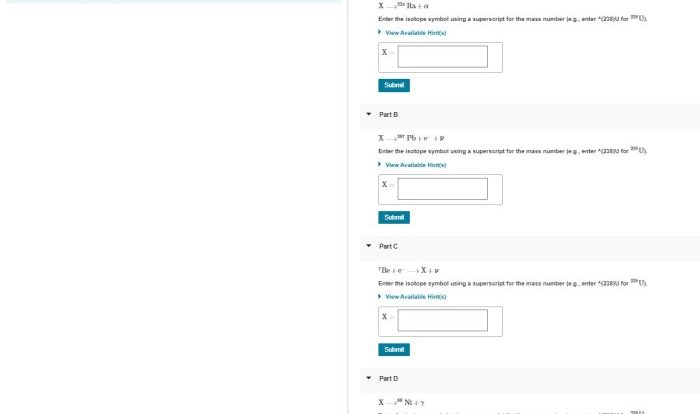
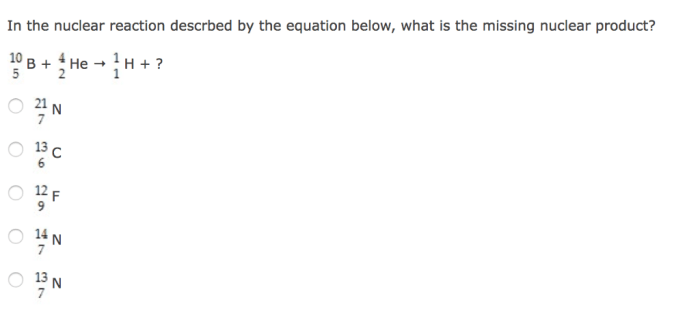The nuclear equation is incomplete.what particle completes the equation – The nuclear equation is incomplete. What particle completes the equation? This intriguing question has captivated scientists for decades, driving groundbreaking research and shaping our understanding of the atomic realm. Join us as we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of incomplete nuclear equations, exploring the methods used to identify the missing particle and its profound implications in nuclear physics.
Nuclear equations, representing the transformations of atomic nuclei, often present themselves as incomplete puzzles. The absence of a crucial particle leaves a void, hindering our ability to fully comprehend the nuclear reaction. Identifying this missing particle is paramount, as it holds the key to unlocking the secrets of nuclear processes and their applications.
Incomplete Nuclear Equations
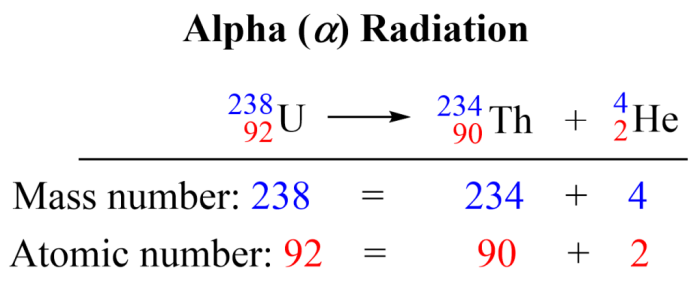
Nuclear equations describe the changes in the atomic nuclei of atoms. They involve the transformation of one atomic nucleus into another, often accompanied by the release or absorption of energy.
Incomplete nuclear equations are equations where one or more of the particles involved in the reaction is unknown. Identifying the missing particle is crucial for understanding the nuclear process and its implications.
Identifying the Missing Particle
- Conservation Laws:Conservation laws, such as the conservation of mass, energy, and charge, provide constraints on the possible particles that can complete the equation.
- Experimental Data:Analysis of experimental data, such as the energies and momenta of the particles involved, can help identify the missing particle.
- Theoretical Models:Theoretical models of nuclear reactions can predict the possible particles that can complete the equation based on known nuclear properties.
Conservation Laws in Nuclear Equations
- Law of Conservation of Mass:The total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products.
- Law of Conservation of Energy:The total energy of the reactants must equal the total energy of the products.
- Law of Conservation of Charge:The total charge of the reactants must equal the total charge of the products.
Applications of Incomplete Nuclear Equations, The nuclear equation is incomplete.what particle completes the equation
- Nuclear Physics Research:Incomplete nuclear equations are used to study the properties of atomic nuclei and the interactions between them.
- Nuclear Power Plants:Understanding incomplete nuclear equations is essential for designing and operating nuclear power plants safely and efficiently.
- Medical Applications:Incomplete nuclear equations are used in medical imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET), to diagnose and treat diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions: The Nuclear Equation Is Incomplete.what Particle Completes The Equation
What is the significance of identifying the missing particle in a nuclear equation?
Identifying the missing particle is crucial because it allows us to fully understand the nuclear reaction, determine the energy released or absorbed, and predict the behavior of the resulting nuclei.
How are conservation laws used to identify the missing particle?
Conservation laws, such as the conservation of mass, energy, and charge, provide essential constraints that help narrow down the possible candidates for the missing particle.
What are some applications of incomplete nuclear equations?
Incomplete nuclear equations play a vital role in nuclear power plants, where they are used to calculate the energy output and optimize reactor design. They also find applications in nuclear medicine and research.